 Yesterday, we talked about whether the labor market would balance in the short term. We also discussed whether there were enough people outside the labor force who might move back in, with higher wages and other inducements, to provide enough bodies to not only fill the current vacancies but also provide enough of a cushion to prevent further dislocations in the future. Although it is close, so far the numbers suggest there are enough people out there to do that. In the next year or so, jobs and employees should move back into a rough equilibrium.
Yesterday, we talked about whether the labor market would balance in the short term. We also discussed whether there were enough people outside the labor force who might move back in, with higher wages and other inducements, to provide enough bodies to not only fill the current vacancies but also provide enough of a cushion to prevent further dislocations in the future. Although it is close, so far the numbers suggest there are enough people out there to do that. In the next year or so, jobs and employees should move back into a rough equilibrium.
The fact that the balance is so close—combined with what we learned earlier about the changing demographic trends and the rising power of labor—suggests that even if the labor market moves back into balance in the short term, that balance remains under threat in the long term. Today, I want to discuss what we know about the next 10 years, which promises to look more like the recent past than the decade before that.
Do Jobs Grow with the Economy?
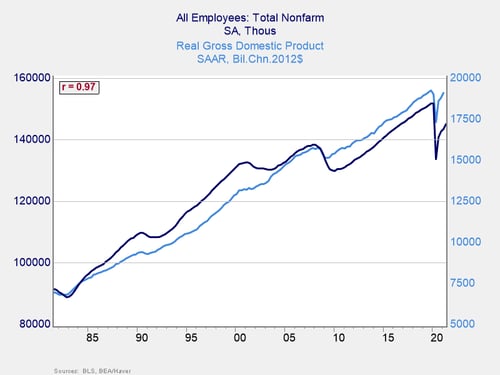
To set the stage, let’s start with something pretty basic. Do jobs grow with the economy? The answer, according to the chart below, is yes. With a 97 percent correlation, a larger economy means more jobs. The correlation is not direct, as the scales for each are different. But, on average over the past 40 years, a 3 percent growth in the economy has meant roughly a 1 percent increase in the number of jobs.
Labor Shortage Ahead?
Looking out over the next 10 years, if we expect real economic growth of about 2 percent per year, then we will have about 7 percent more jobs to be filled. Taking that and matching it with our analysis so far, the question is, will we have 7 percent more workers to fill those jobs and keep labor markets in balance?
The answer is no. According to the Bureau of the Census, which does forecasts, the working-age population is projected to increase from 215,645,000 in 2022 to 219,554,000 in 2032—an increase of just under 4 million, or about 1.8 percent. Over the same time period, the number of jobs would increase by 7 percent from the current level of approximately 153 million, which would be about 11 million. In sum, 10 years from now, we will need 11 million more workers to fill those jobs, and we will have less than 2 million. And that assumes everyone is working, which will not be the case. While we will get back to balance in the short term, then, the trends of the past two decades are going to continue, and labor shortages will only get worse over the next decade.
That is, of course, if everything stays the same. It won’t. So, the next question in the analysis becomes how will companies deal with this?
What Can Companies Do?
More people. There are a couple of options. Adding people is the first, whether that means increased immigration here in the U.S. or increased outsourcing to other parts of the globe. Immigration is a nonstarter here, in the amounts that will be needed. So, outsourcing will come back into vogue sometime in the next five years or so. It will not be China this time, as it is facing the same demographic issues we are, except China's are much worse. There are other options though, notably India (which everyone knows about) and Africa (which no one is talking about). My bet would be on Africa, which has more people and will desperately need the jobs.
Even when we do outsource, though, it will not solve the problem. Remember, the number of total jobs in the U.S. increased substantially, even as tens of millions were outsourced to China. We will see the same increase even if we send jobs to Nigeria this time around. We will not be able to outsource our way out of the problem.
Automation. The other option is automation, taking jobs and replacing them with machines. We are already seeing this, of course, with automated checkout at the grocery store and screen ordering at McDonald’s. Expect it to increase. This will not be a panacea, however, as someone needs to install, program, and so forth all of those machines, which means more jobs. Again, there has been extensive automation in recent decades, even as the number of jobs has increased. Automation will not be a magic bullet either.
What’s Next?
Any way you look at it, the labor market will be very different—and more favorable to workers—over the next decade. Any way you look at it, that change will affect the economy—and our investments. So, what do we do? We will take a look at that over the next couple of weeks.


 Print
Print

