 In my post on Friday, I noted that employment is, in many ways, approaching boom times. Although it’s not there yet—the proportion of part-time jobs and the level of high-paying jobs continue to be concerns—employment is moving in the right direction and doing so at an increasing rate.
In my post on Friday, I noted that employment is, in many ways, approaching boom times. Although it’s not there yet—the proportion of part-time jobs and the level of high-paying jobs continue to be concerns—employment is moving in the right direction and doing so at an increasing rate.
The missing piece here has been wage inflation. If things are so good, why aren’t we all making more money? In fact, there are good reasons to think that the lack of wage growth so far is not a systemic problem, and that growth will show up in the reasonably near future.
Employment data suggests wage growth in the next 12 months
Quits rate. The first thing to consider is how many people are quitting their jobs. The more voluntary quits, the more confidence people have in finding a new job, and the more employers have to pay in order to keep good workers. The chart below shows that wage growth tends to follow the quits rate with a one-year (12-month) lag. The correlation is 89 percent, which is excellent for an economic data series, and it makes intuitive sense as well.
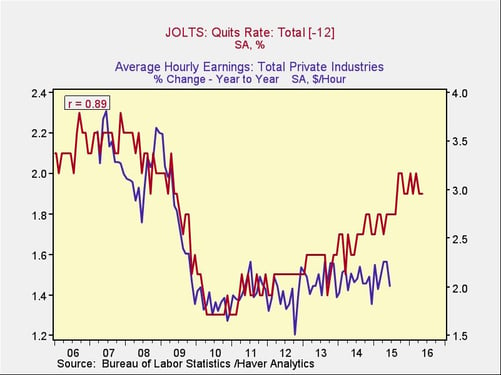
You can see that a gap has opened up between quits and the wage growth series, which suggests that either quits have to drop (unlikely, as the employment market continues to strengthen) or wage growth has to rise.
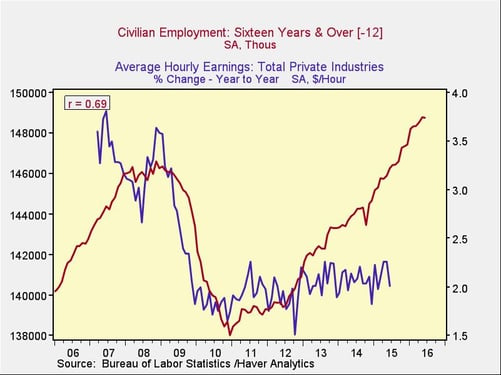
Total employment. The second indicator worth looking at is total employment. Again, on a commonsense basis, the more people are hired, the more difficult it will be to hire the next person—and the more employers will have to pay. Here again, we see a strong relationship (a 69-percent correlation) that also makes sense intuitively. And here again, we have a widening gap. Either employment will drop or wage growth will increase.
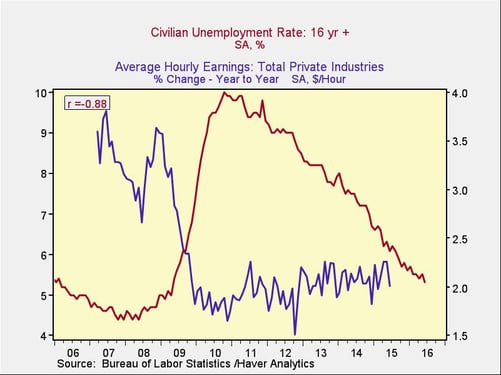
Unemployment rate. Another way to look at this data is to compare the unemployment rate with wage growth, which gives substantially similar results. In fact, we see that the unemployment rate has reached the levels of the mid-2000s, but wage growth has not recovered. Why?
I suspect the answer is shown in the following chart, which incorporates the difference between the underemployment rate and the unemployment rate and also captures some of the part-time and slow high-wage job growth effects I discussed in my previous post.
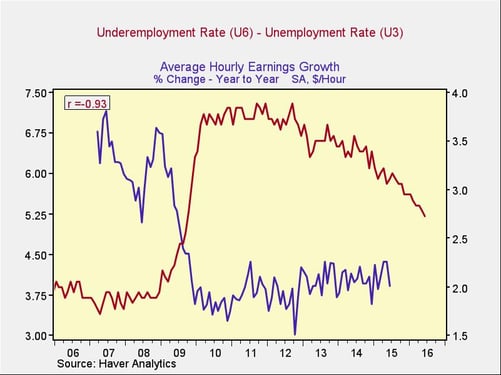
You can see that the normalized difference between the two was around 3.5 percent and 4 percent in the mid-2000s and now stands at around 5.25 percent.
This excess labor supply, captured in the underemployment survey but not in the unemployment numbers, appears to be the major reason for slow wage growth so far. Looking at the way it has evolved over time, the decline appears to be accelerating slightly, which suggests that it should normalize in the next 12 months or so, presumably forcing wage growth upward.
But we could see growth even sooner
All of the above presupposes that wage growth is, in fact, stuck in a slump and suggests a recovery in the next 12 months or so, but wages may grow more quickly than these figures would indicate. The average hourly earnings numbers have several weaknesses, so it’s worth looking at some different indicators.
The most important of these is the Employment Cost Index, which takes into account all compensation costs, such as benefits, rather than just wages. You can see here that the ECI has generally tracked average hourly earnings, but it has jumped up in the past year or so.
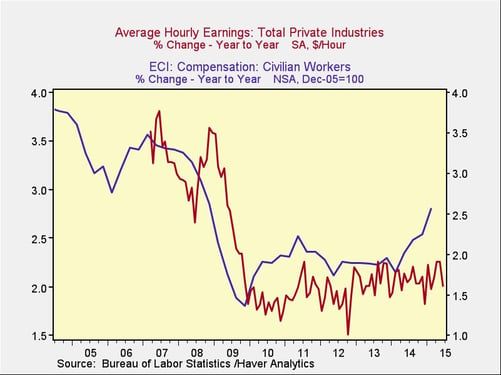
Arguably, this is because of the cost of the Affordable Care Act, aka Obamacare, which has increased compensation costs and possibly made businesses less able to afford wage increases. If this is the case, that shock may be fading and normal wage growth likely to resume.
The other important indicator for pending wage growth is the actions of actual businesses. Walmart, Target, and McDonalds, major corporations with large workforces in the sectors that have exhibited the slowest wage growth, have all announced significant pay raises for their workers. I suspect they’re not driven by altruism but rather by a perception that the employment market has improved enough that they must give raises to retain people—and that is exactly what we’ve been waiting for.
Overall, although the problem of missing wage growth remains, almost all indicators show that it’s coming—and may already be here, albeit in something of a disguise. We need to keep an eye on this, particularly if wage growth is still missing in about a year. For the moment, though, conditions seem to be evolving as they should, even if not as we would wish them to.


 Print
Print

