 My colleague Sam Millette, senior investment research analyst on Commonwealth’s Investment Management and Research team, has helped me put together this month’s Market Risk Update. Thanks for the assist, Sam!
My colleague Sam Millette, senior investment research analyst on Commonwealth’s Investment Management and Research team, has helped me put together this month’s Market Risk Update. Thanks for the assist, Sam!
It’s time for our monthly look at market risk factors. Just as with the economy, there are several key factors that matter for the market in determining both the risk level and the immediacy of the risk. Although stocks remain close to all-time highs, recent volatility is a reminder that, given valuations and current market behavior, it is useful to keep an eye on these factors.
Recession risk
Recessions are strongly associated with market drawdowns. Indeed, 8 of 10 bear markets have occurred during recessions. As we discussed in this month’s Economic Risk Factor Update, right now the conditions that historically have signaled a potential recession are not in place. There are, however, signs that the risk is growing, with consumer and business confidence weakening and a continued yield curve inversion. On an absolute basis, most of the major signals are not yet in a high-risk zone. But trends are becoming more negative, and four of the signals are now at yellow, with two trending toward red. As such, we have kept economic factors at a yellow light for September.
Economic shock risk
There are two major systemic factors—the price of oil and the price of money (better known as interest rates)—that drive the economy and the financial markets, and they have a proven ability to derail them. Both have been causal factors in previous bear markets and warrant close attention.
The price of oil. Typically, oil prices cause disruption when they spike. This is a warning sign of both a recession and a bear market.
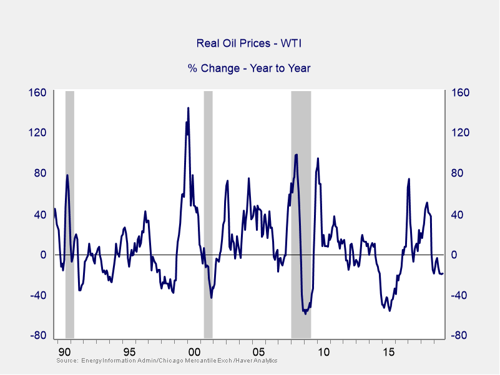
Quick price spikes, like we saw in both 2017 and 2018, are not necessarily indicators of trouble, especially if prices subsequently decline and take us well out of the risk zone. Last month’s drone attack on a major Saudi Arabian oil production facility likewise caused prices to spike, but they have already come back to pre-attack levels, sitting well below 2018 highs and down on a year-to-date basis. Therefore, this indicator remains at a green light.
Signal: Green light
The price of money. I cover interest rates in the economic update, but they warrant a look here as well.
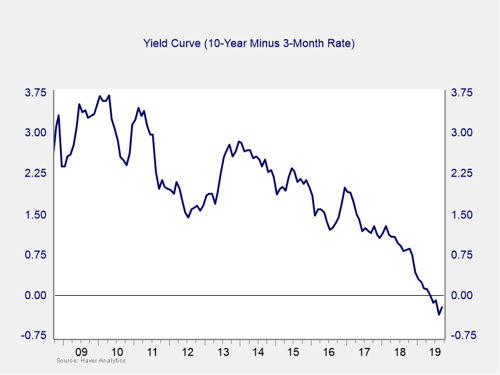
The yield curve remained inverted in September, despite an increase in long-term rates during the month. The 10-year Treasury yield rose from 1.47 percent to start the month to 1.68 percent at month-end. Yields on the short end of the curve fell during the month, as the Fed cut the federal funds rate at its September meeting by 25 bps, as expected. Meanwhile, the yield on the 3-month Treasury fell from 1.98 percent at the start of the month to 1.88 percent by month-end. Market participants widely expect the Fed to cut the federal funds rate by another 25 bps in December.
As the length of the inversion grows, it is getting close to starting a recession countdown. But it is not quite there yet. Given that, and the delay between such an inversion and the actual start of a recession, the immediate risk remains low. As such, along with other signs of weakness, the indicator remains something to watch. We are keeping this measure at a yellow light this month, with a shade of red.
Signal: Yellow light (trending to red)
Market risk
Beyond the economy, we can also learn quite a bit by examining the market itself. For our purposes, two things are important:
- To recognize what factors signal high risk
- To try to determine when those factors signal that risk has become an immediate, rather than theoretical, concern
Risk factor #1: Valuation levels. When it comes to assessing valuations, I find longer-term metrics—particularly the cyclically adjusted Shiller P/E ratio, which looks at average earnings over the past 10 years—to be the most useful in determining overall risk.
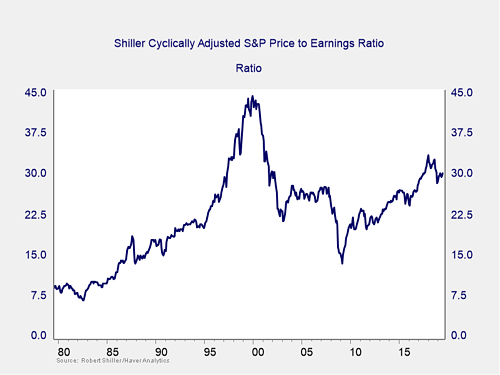
This is the same data that was presented last month. The major takeaway from this chart is that despite the recent decline, valuations remain extremely high. They are still above the levels of the mid-2000s, although down from recent highs. Also worth noting, however, is the very limited effect on valuations of the pullback in stock prices to start the summer. Despite the drop, stocks remain quite expensive based on history. High valuations are associated with higher market risk—and longer-term metrics have more predictive power. So, this is definitely a sign of high risk levels.
Even as the Shiller P/E ratio is a good risk indicator, however, it is a terrible timing indicator. To get a better sense of immediate risk, we can turn to the 10-month change in valuations. Looking at changes, rather than absolute levels, gives a sense of the immediate risk level, as turning points often coincide with changes in market trends.
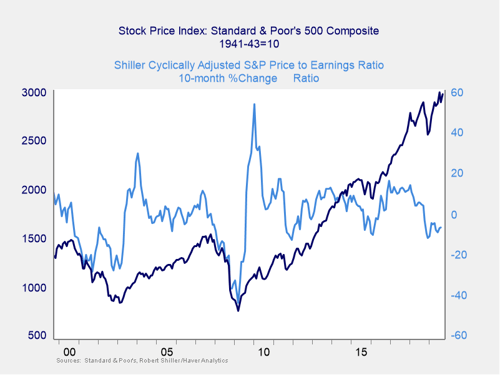
Here, you can see that when valuations roll over, with the change dropping below zero over a 10-month or 200-day period, the market itself typically drops shortly thereafter. After the decline at the end of last year took the market into the risk zone, recovery through the first half of the year took us back close to even. September was a positive month for markets following August’s volatility. We are keeping this indicator at yellow due to the fact that we remain down on a year-to-year basis, just as in 2011 and 2015–2016.
Signal: Yellow light
Risk factor #2: Margin debt. Another indicator of potential trouble is margin debt.
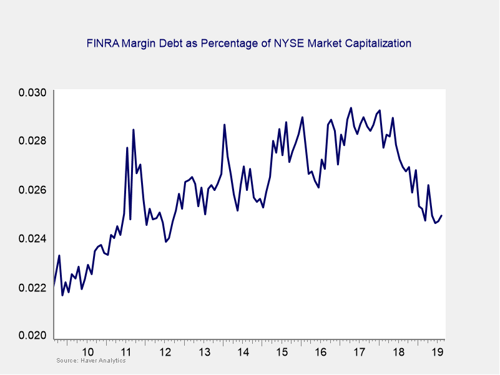
Debt levels as a percentage of market capitalization have dropped substantially over the past year and remain close to the lowest levels of the recovery. Although margin debt remains at the low end of recent history, it is still high by historical standards. The overall high levels of debt are concerning; however, as noted above, high risk is not immediate risk.
For immediate risk, changes in margin debt over a longer period are a better indicator than the level of that debt. Consistent with this, if we look at the change over time, spikes in debt levels typically precede a drawdown. The most recent uptick in margin debt as a percentage of market capitalization still leaves this ratio well below highs seen in 2017 and 2018.
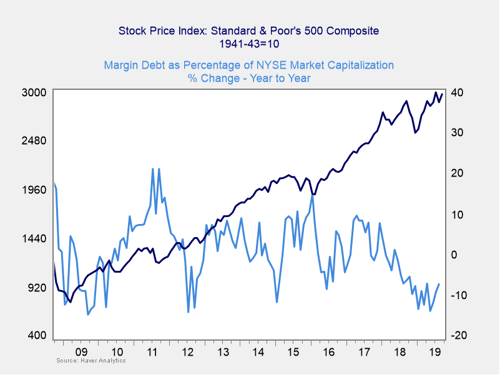
As you can see in the chart above, the annual change in debt as a percentage of market capitalization remains well below zero, and it seems to be on a general downward trend despite last month’s uptick. This indicator is not signaling immediate risk at this point but has been volatile in recent months. Given that, and the fact that the overall debt level remains very high, it is worth watching. So, we are keeping this indicator at a yellow light.
Signal: Yellow light
Risk factor #3: Technical factors. A good way to track overall market trends is to review the current level versus recent performance. Two metrics I follow are the 200- and 400-day moving averages. I start to pay attention when a market breaks through its 200-day average, and a break through the 400-day often signals further trouble ahead.
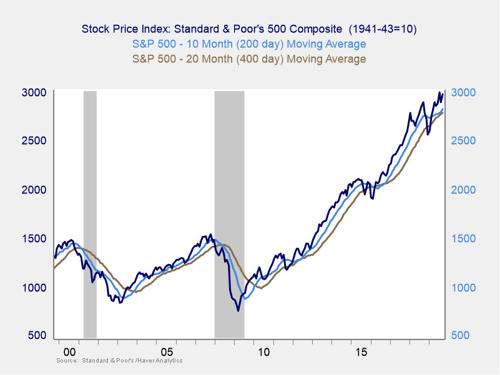
Last year’s declines took all three major U.S. indices below the 400-day trend lines, a significant support level. The subsequent recovery brought them back above both that level and the 200-day level. But in May, we had a brief break back below the 200-day trend line, followed by a recovery, and then another brief break below in June. Following declines in August, September’s positive results helped calm fears of a pullback below the trendline. The probability that the markets continue to rebound is still the base case, but as we saw in August volatility can strike at any time, so we are leaving this indicator at yellow.
Signal: Yellow light
Conclusion: Market risks moderate, but economic risks rising
Market risks have been at the yellow light level for the past 19 months and recently dropped even further with the hint of some red lights. But market conditions have largely improved over the past couple of months, despite August’s turbulence. On the other hand, economic risks have risen as the incoming data remains weak, and there have been a couple of potentially significant breakdowns. On balance, this leaves us solidly in the yellow zone of increased risks.
The market recovery following August’s volatility is encouraging, and the overall economic environment remains supportive. While neither of the likely shock factors is necessarily indicating immediate risk, the rising signs of economic weakness, combined with the fact that several of the market indicators continue to point to an elevated level of risk, suggest that recent volatility may continue. The recovery to start the month is encouraging, but as we saw last month outside factors can swiftly impact markets.
As such, we are keeping the overall market indicator at a yellow light. This is not a sign that risks have passed. Instead, it is a recognition that despite the recent market turmoil, basic conditions remain supportive and that while risks are real, the most probable course is more appreciation—even though further volatility is quite likely.



 Print
Print

