 I have revamped the monthly market risk update this month to incorporate a wider range of factors and, I hope, a more useful presentation style. My economic risk factor update seems to have wide appeal, so I am going to use the same traffic light system here, as well as incorporate some economic metrics outside the market.
I have revamped the monthly market risk update this month to incorporate a wider range of factors and, I hope, a more useful presentation style. My economic risk factor update seems to have wide appeal, so I am going to use the same traffic light system here, as well as incorporate some economic metrics outside the market.
Market risks come in three flavors: recession risk, economic shock risk, and risks within the market itself. Thus far, this update has dealt only with the latter, but I think it makes sense to incorporate the former as well, for a more inclusive look at what the risks are.
Please let me know what you think—along with any changes you feel might be useful.
Recession risk
As I mentioned in yesterday’s economic risk factor update, we’re still in green-light territory when it comes to recession risks. The conditions that might lead to a recession simply are not there.
Economic shock risk
There are two major systemic factors—the price of oil and the price of money (better known as interest rates)—that drive the economy and financial markets and that have a proven ability to derail them. Both have been causal factors in previous bear markets and warrant close attention.
The price of oil. Oil prices typically cause a disruption when they spike. Spiking oil prices are a warning sign of both a recession and a bear market.
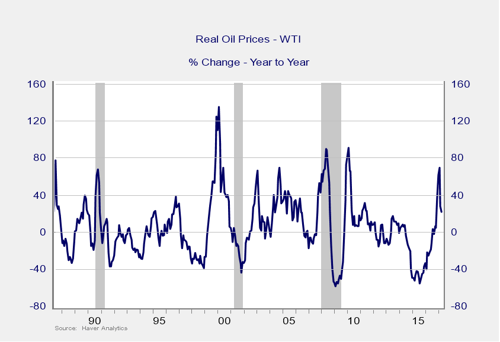
Signal: Yellow light
Right now, per the chart, the percentage increase in the real oil price is in the danger zone, although it has dropped recently. Since this is in percentage terms, and the price of oil remains low in dollar terms, I don’t necessarily think this is a risk factor. On the other hand, it certainly takes oil prices from a substantial tailwind to at least neutral and is therefore a negative factor.
Overall, this indicator is at yellow light status.
The price of money. I cover interest rate risk in the economic update, but it warrants a look here as well.
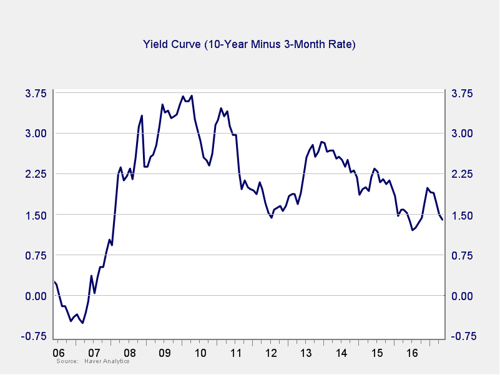
Signal: Green light (with a shade of yellow)
The yield curve flattened further in May, caused by lower inflation data that depressed the intermediate and long portions of the interest rate curve. This flattening may continue, as the market widely expects the Federal Reserve to raise short-term rates at the mid-June meeting.
Although the spread between the 10-year and 3-month rates remains far outside the risk zone, we are getting close to the lowest levels we’ve seen since the crisis. If and when the Fed does raise short-term rates, there is a real chance the spread could drop further. Overall, monetary policy is providing less support to financial markets, and the trend may well get worse.
This indicator is still a green light, but it will bear watching over the next couple of months, so I am adding a shade of yellow.
Market risk
Beyond the economy, we can also learn quite a bit by examining the market itself. For our purposes, two things are important:
- To recognize what factors signal high risk
- To try to determine when those factors signal that risk has become an immediate, rather than a theoretical, concern
Risk factor #1: Valuation levels. When it comes to assessing valuations, I find longer-term metrics—particularly the cyclically adjusted Shiller P/E ratio, which looks at average earnings over the past 10 years—to be the most useful in determining overall risk.
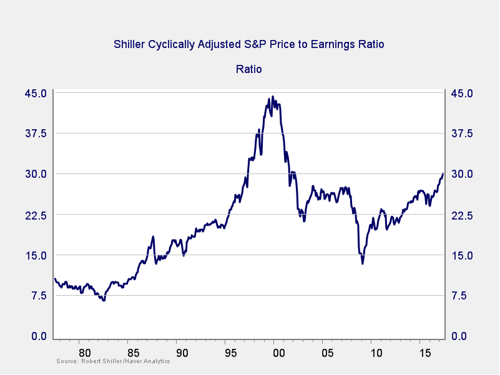
This first chart is interesting for a few reasons. In the aftermath of November’s presidential election, we can see that equity valuations have increased to levels of the early 2000s. Recent gains have pushed valuations even higher, to the third-highest level of all time. We’re now just below levels of 1929 and, as you can see from the chart, 1999.
Nevertheless, valuations remain below those peaks, so you might argue that this metric does not suggest immediate risk. Of course, that argument also assumes we might be headed back to 2000 bubble conditions, which isn’t exactly reassuring.
What would give us a better idea of timing? We can look at changes in valuation levels over time instead of at absolute levels.
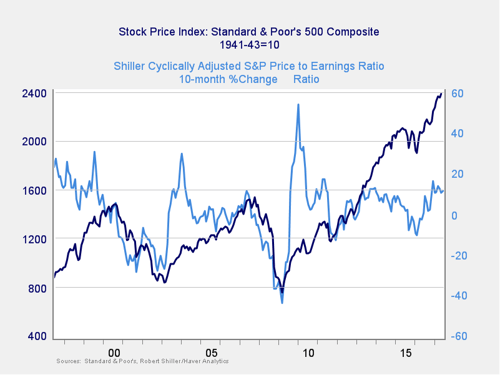
Signal: Green light
Here, you can see that when valuations roll over, with the change dropping below zero over a 10-month or 200-day period, the market itself typically drops shortly thereafter. The rally since the election has kept changes in valuations at a healthy positive level. And although the level of change seems to be moderating, it is well above the trouble zone. Therefore, this indicator shows low immediate risk and can be considered a green light.
Risk factor #2: Margin debt. Another indicator of potential trouble is margin debt.
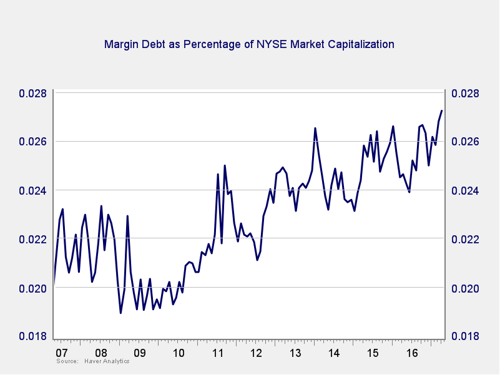
Debt levels as a percentage of market capitalization have moved back to all-time highs in recent months, which raises the risk level considerably. While concerning, as I mentioned above, high risk doesn’t necessarily equate to immediate risk.
When looking to identify immediate risk, changes in margin debt are a better indicator than the overall level of that debt. Consistent with this, if we look at the change over time, spikes in debt levels typically precede a drawdown.
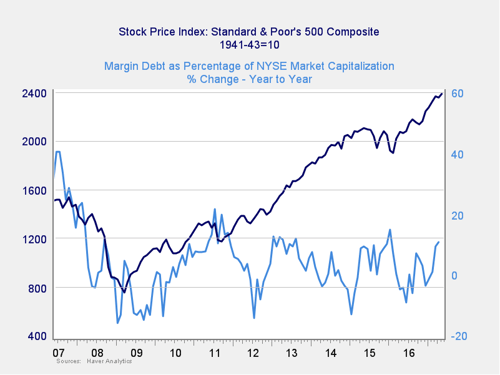
Signal: Yellow light
As you can see in the chart above, the change in debt as a percentage of market capitalization has moved higher, although it has not yet broken above the level that has signaled trouble in the past. It is, however, much closer to the risk zone than it has been, and the risk is increasing. Combined with the high absolute level of margin debt, therefore, the risk level is becoming more immediate.
Risk factor #3: Technical factors. A good way to track overall market trends is to review the current level of the market versus recent performance. Two metrics I follow are the 200- and 400-day moving averages (MAs). I start to pay attention when a market breaks through its 200-day MA, and a break through the 400-day MA often signals further trouble ahead.
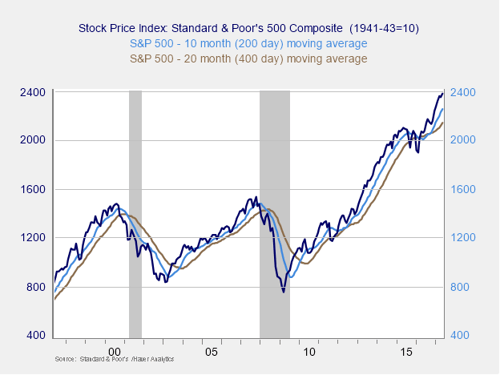
Signal: Green light
As illustrated in the above chart, both of these indicators remain positive, with the S&P 500 well above both trend lines. Even as markets continue to reach new highs, it’s quite possible that the advance will continue given growth in earnings and positive consumer, business, and investor sentiment. A break into new territory could actually propel the market higher, despite the high valuation risk level. With the index well above the trend lines, the likely trend continues to be positive.
Conclusion: Conditions weakening but remain favorable overall
The overall economic environment remains supportive, and neither of the likely shock factors are necessarily indicating immediate risk. Similarly, although several of the market indicators point to an elevated level of risk, that risk does not look to be immediate. So, although risk levels have increased moderately, the market environment appears favorable in the near term, and we remain at a green light for this month.



 Print
Print


