 Student loan debt has increased dramatically in recent years, and as graduates reportedly struggle to find jobs, there's growing concern about the role these loans might play in the next financial crisis. The fear is that a systemic default could rock the financial system, much as subprime mortgage defaults did.
Student loan debt has increased dramatically in recent years, and as graduates reportedly struggle to find jobs, there's growing concern about the role these loans might play in the next financial crisis. The fear is that a systemic default could rock the financial system, much as subprime mortgage defaults did.
Do we really have a systemic problem on our hands? And just how great is the risk? Let’s take a look at the underlying data.
The big picture: student loan growth normalizing
We’ll start by comparing student loans and general consumer debt, as shown in the following chart.
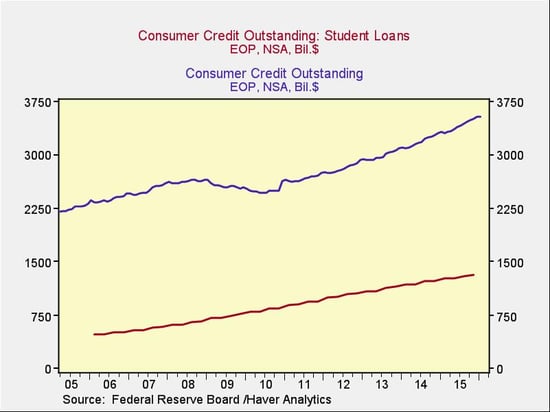
Two things stand out here:
- First, student loans represent a substantial proportion of consumer debt.
- Second, overall consumer debt grew faster than student loans before and after the crisis; during the crisis, however, general consumer debt declined while student debt continued to increase. The chart below shows the annual rate of increase for both.
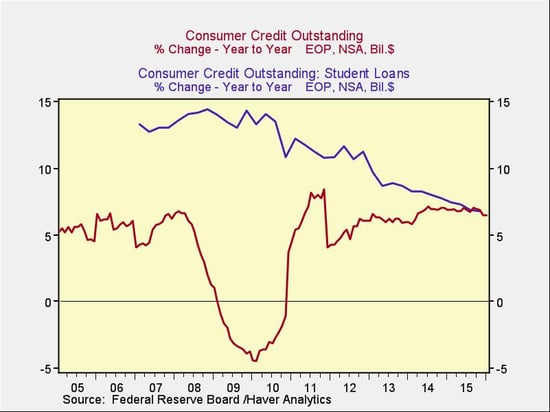
As you can see, student loan growth has recently declined to the level of general consumer debt growth, suggesting that it is normalizing. Even if it is a problem, at least that problem isn’t growing at an undue rate.
In fact, it should be shrinking. In the chart below, we can see that, after increasing as a percentage of total consumer debt, student loan debt has started to drop. (Note that the increase was due to a drop in general consumer credit during the crisis, rather than to an explosion in student borrowing.)
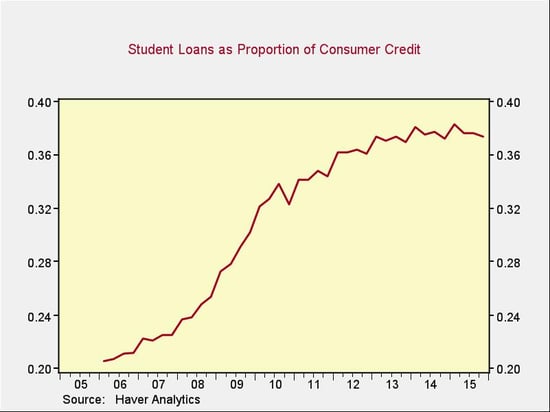
Although student loans have grown at a fast rate, giving rise to the concern, they are now normalizing, even as other consumer borrowing picks up.
A demographic explanation for ballooning growth
The next question is whether that fast growth rate was based on the crisis, on students borrowing more, or on some other factor. An obvious potential reason is demographics. As the millennial generation moved into their college years, you’d expect debt growth to increase as well, simply as a function of more students, and that is what we see in the following chart. (Note the 91-percent correlation between population changes and the student loan growth rate.)
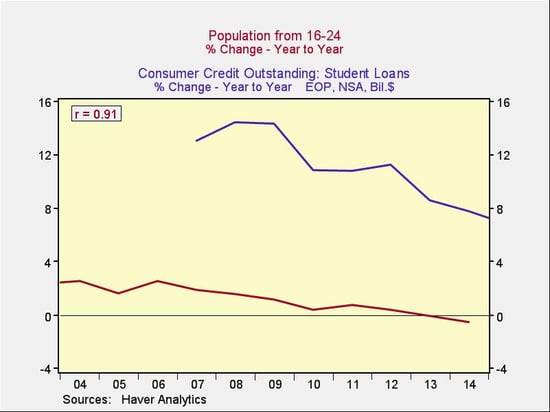
Overall, the growth rate in student loans, while high during the crisis, was largely driven by demographic changes and is even now dropping back to more normal levels.
Nonetheless, student loan debt may still be a risk, especially given the high proportion of student debt as a percentage of consumer debt. In order to spark a crisis, those loans must first default and, second, be unrecoverable.
When considering default, the size of the loan is an obvious risk factor. Take a look at this chart, from the Federal Reserve via Wikipedia:
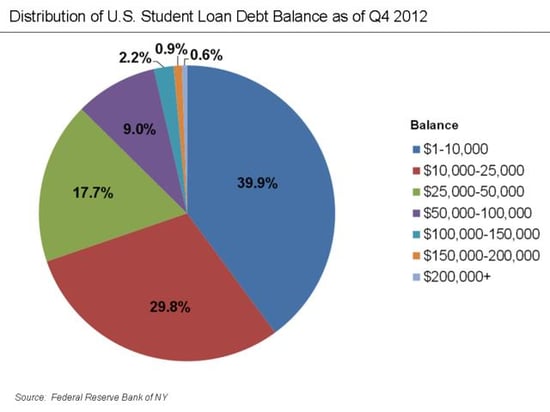
Here, we see that:
- More than two-thirds of the loan balances are less than $25,000. Most graduates should be able to manage this, if employed.
- More than five-sixths of the loan balances are less than $50,000. Again, while burdensome, this is reasonably manageable by graduates, if employed.
- Less than 15 percent of loan balances are in the highest-debt tranches, which includes various medical, business, and other costly professional programs that may provide the means to repay the debt.
Overall, then, the individual loans do not appear to be impossible to repay. The big caveat here is that, in order to repay even a small loan, the graduate has to be employed at a reasonable salary. The following chart shows the unemployment rate for those ages 20 to 24, which covers the group completing postsecondary education.
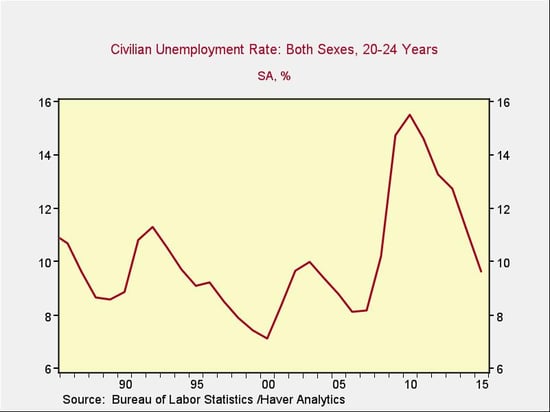
There has been a serious decline in unemployment for this cohort over the past five years, to levels consistent with much of the 1990s and some of the 2000s. Plus, for our purposes, these figures represent a worst case, since we must consider only those with postsecondary education to incur student debt. With that in mind, let’s take a look at the longer-term employment results of that education.
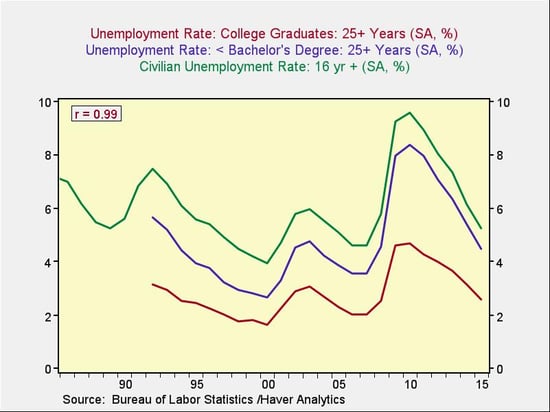
Clearly, younger people are doing better, and in aggregate, the more educated are doing better yet, suggesting that growing employment should help ensure student debt repayments.
A burden for many, but not a systemic risk
Overall, the spike in student loan growth can largely be chalked up to demographics. With millennials now graduating, loan growth is normalizing. Average loans are, in general, supportable if the graduate is employed, and the employment market for the millennial cohort has improved dramatically over the past five years—and even more so for those with the education that the student loans funded.
Although there's no doubt that many are struggling on an individual basis, student loans do not appear to represent a systemic threat, based on the underlying ability of students to afford and pay back their loans.
Also acting as a safeguard against systemic problems, many, if not most, of these loans were cosigned by parents, who are also liable for repayment if the student defaults. Again, while this will certainly be a hardship for some, it does substantially reduce the potential for a crisis.
Any form of debt represents a risk, but the risk from student loans doesn't warrant the concern many are expressing. There will certainly be defaults—probably many of them—but the system as a whole should be just fine.


 Print
Print


