 I’ve spent the past couple of posts painting a picture of how dire the situation is with the deficit and the debt—and it really is. But now we can turn to the real questions: is this a solvable problem or not? If so, what would it take? Indeed, there are a couple of ways the problem can be solved. Some are painless and others not so much. Let’s start with the easy ones.
I’ve spent the past couple of posts painting a picture of how dire the situation is with the deficit and the debt—and it really is. But now we can turn to the real questions: is this a solvable problem or not? If so, what would it take? Indeed, there are a couple of ways the problem can be solved. Some are painless and others not so much. Let’s start with the easy ones.
Faster growth
A deficit is not necessarily a problem over time. If the economy continually grows faster than the deficit, then the debt as a percentage of the economy as a whole will go down. In other words, if the deficit is around 2 percent but the economy is growing at 3 percent, then the ability to pay the accumulating debt will be there. It is only when deficit growth is faster than economic growth—where you will not have the ability to pay—that a deficit becomes a problem. This points us to one potential solution, which is to grow the economy faster.
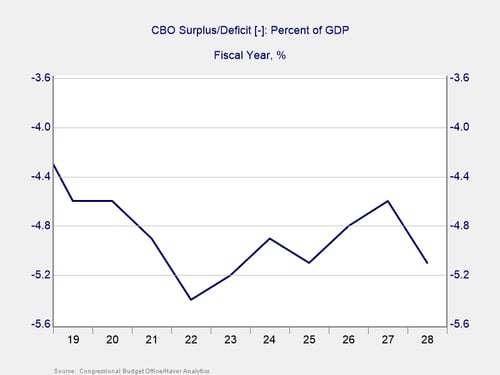
As you can see in the chart above, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) expects a deficit of around 5 percent of GDP over the next 10 years. In theory, if we could grow the economy at 5 percent or better, that would leave the debt burden where it is now, as a percentage of the economy. This, in fact, is one of the major justifications of the tax cuts: that they will boost growth and more than support the additional deficit spending they create.
The problem, as you can see in the chart below, is that on a year-to-year basis, growth has averaged around 2.5 percent over the past 20 years. Plus, it has hit the 5-percent target only once, in the second quarter of 2000. Growth alone is not going to do it.
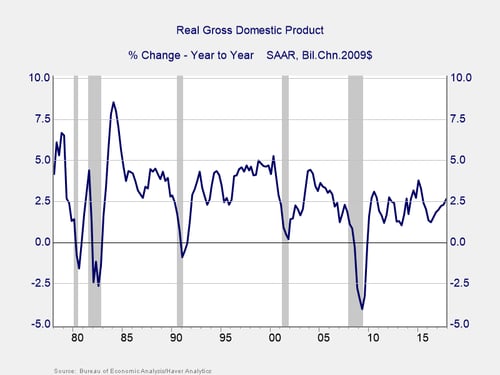
This analysis does point out, however, that some level of deficit is acceptable, as the additional debt will be supported by a larger economy. So, we don’t have to eliminate the entire deficit, just trim it down to match the economy’s ability to grow. Right now, based on projected growth, a sustainable deficit would probably be in the range of $350 billion, using a $20 trillion economy and projected growth (by the CBO) of around 1.75 percent.
This reasoning may seem counterintuitive. But it is true—as proven by the recent fiscal cliff confrontation and subsequent sequestration cuts to federal spending. We continued to run a deficit but of less than the economic growth rate, and the problem went away for a while.
Spending cuts and revenue increases
The problem, then, will not be completely solved by growth. But it will be partially solved. We still, however, have some way to go. Given the acceptable level of the deficit based on current numbers (guesstimated at $350 billion) and the $700 billion deficit in 2017, we therefore still need about $350 billion in some combination of revenue increases and spending cuts.
Based on the CBO numbers, it would take a 10-percent revenue (tax) hike across the board to solve the problem with taxes alone—or about a 25-percent cut in discretionary spending with spending cuts alone. Discretionary spending includes the military and everything else the government does, but it does not include social security or Medicare. Evenly splitting the adjustments between spending cuts and revenue increases, we get a 5-percent revenue hike plus a 13-percent spending cut.
Neither of these solutions is easy, and both sides would be screaming. But there are ways to make them easier, such as phasing them in over a period of 5 to 10 years. With inflation, you wouldn’t even have to cut spending; you could just hold it constant, and let the real cost erode over time.
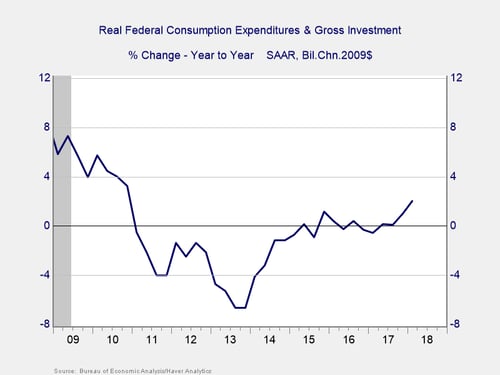
As I have mentioned, there is precedent for this approach. In the sequester, as shown above, we did see real spending cuts at the federal level and then a long period of flat real spending.
So, is the deficit and debt problem solvable?
This brings us to the final answer to our question of whether the deficit and debt problem is solvable. The answer is “yes,” with a moderate tax increase and moderate spending cuts. Note that solvable does not mean easy or pleasant—it won’t be. Note also that this analysis was based on 2017 numbers, and the recent tax cuts and spending increases have moved us further away from a solution. So, any actual needed changes will be worse. It won’t be fun, and everyone will hate it.
It also won’t happen until the pain of the solution, which is considerable, becomes less than the pain of the problem. That might not be for some time. The problem—and the pain of the solution—will be worsening every year. Nonetheless, it is important to realize that there is a solution out there, available when we are ready to take it. By all means, pay attention and be concerned. But don’t panic, not just yet.


 Print
Print

