 Today's post is from Peter Essele, manager of Commonwealth's Investment Management and Research team.
Today's post is from Peter Essele, manager of Commonwealth's Investment Management and Research team.
A little over a year ago, my colleague, Anu Gaggar, and I conducted a study for the Independent Market Observer. We examined the emerging markets and international asset classes through the lens of investor behaviors, noting at the time that many investors had shed these asset classes during 2016. They did so largely because they feared underperformance and higher volatility. We believed there could be negative consequences on portfolio returns from this decision, however, so we took a closer look.
Today, we're revisiting this topic to see whether investors have changed their minds since then, choosing to once again accept the risks of global diversification. And, if so, what might that mean for their portfolios going forward?
Then and now
Investor aversion to these asset classes is clearly evidenced by the negative flows for 2016 compared with other periods (see Figure 1).
Figure 1. Monthly Flows—International and Emerging Markets Investment Vehicles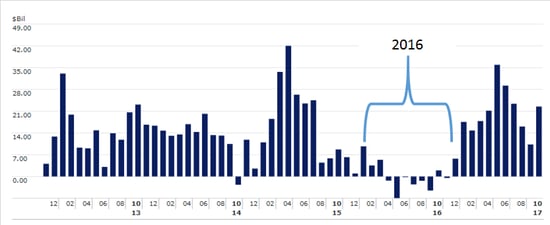
Source: Morningstar Direct, Commonwealth
Fast-forward to May 2017 when more than $35 billion moved into emerging markets and international equities—the second-largest monthly inflow in five years. This purchasing frenzy came at a time when both developed international and emerging markets were outpacing the S&P 500 by roughly 10 percent year-to-date, according to the MSCI EAFE and MSCI Emerging Markets indices.
The relationship between fund flows and subsequent returns
At Commonwealth, we often discuss the inverse relationship between fund flows into an asset class and subsequent returns with our advisors. In many cases, we have found that the larger an asset class’s investment flows over the prior 12 months relative to historical trends, the lower the forward three-year returns are.
The past few years have been a perfect case study of this. Figure 2 illustrates where we overlay investment flow periods alongside performance of developed international equities. For instance, the green areas represent periods of strong investment inflows into foreign equities, and the gold portion represents a stretch of outflows. The blue line is the performance of iShares MSCI EAFE ETF (ticker: EFA) over the past five years.
Figure 2. Price Performance of iShares MSCI EAFE ETF and Investor Behavior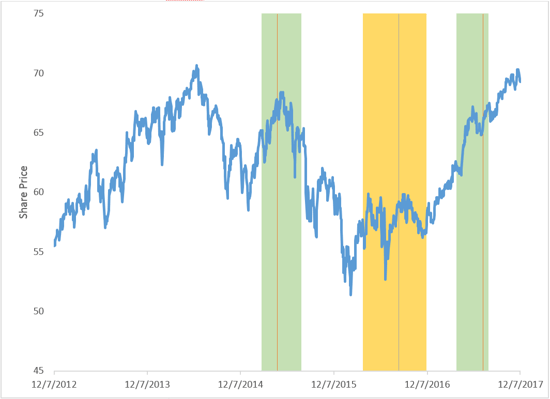
Source: Morningstar Direct, FactSet, Commonwealth
What becomes evident is that investors typically have bought into developed international markets after a price rebound and then sold after a period of underperformance—a strategy that doesn’t bode well for returns over time. (Remember: You want to buy low and sell high.) There is clearly an element of performance chasing occurring with investment decisions in this space, which is a trend we’ve witnessed across other asset classes as well.
This then begs the question: Is there value left in foreign equities, or has the train left the station?
Do foreign equities still have value?
Aside from looking at investor behavior relative to price movements, there are other ways to assess value across securities, asset classes, and geographies. For instance, it’s useful in any analysis to consider fundamentals, technicals, and currency effects in the context of recent price movements.
In tomorrow’s blog post, Commonwealth’s in-house expert on foreign equities, Anu Gaggar, will aim to answer this question and shed further light on foreign markets.
Happy New Year!


 Print
Print

