
Brad here. Today, Rob Swanke, an analyst with Commonwealth’s Investment Management and Research team, shares his insights. Enjoy!
It’s 2020, the beginning of a presidential election year. As the months unfold, the election will likely become the primary market risk to worry about for many people. Democratic primary voting will begin in February with the Iowa caucuses, but only 4 percent of the delegates will be chosen that month. The party’s direction won’t begin to unfold until March 3, when 34 percent of the delegates will be chosen by 14 states. But we still won’t have clarity at that point, as delegates are distributed proportionally for each state by the Democratic Party. With several candidates polling in the double digits, a lot of uncertainty regarding the Democratic nominee may exist right up to the July convention. Although the bull market has lasted more than a decade, will valuations keep moving higher in this uncertain political climate?
Which direction for the Democrats?
The winner of the Democratic primary will be important, as significant policy differences exist between the two wings of the Democratic Party vying to steer its—and the country’s—direction. The current front-runners on the progressive left, Bernie Sanders and Elizabeth Warren, are proposing the biggest changes to health care, education, climate and economic policy, as well as the tax code. Whether the candidate is from the progressive left or the moderate wing will determine the degree of the party’s policy differences from President Trump’s Republican administration. Uncertainty regarding policy conflicts will create considerable angst among investors as November approaches. The market will likely experience some volatility, as participants digest the possibility of an incoming Democratic administration making changes to the tax code for corporations or individuals. Another risk factor is the potential for increasing trade tensions should Trump be reelected.
Control of Congress
Let’s not lose sight of the larger picture, however. The 2020 election is not just about the presidency. There will also be elections in the House and Senate. Both parties will likely face uphill battles for control of each branch of Congress, and neither party is likely to gain a significant advantage. Many House districts aren’t expected to be competitive, and the 2020 Senate map favors Republicans. The separation of power should limit some of the most aggressive party proposals from being implemented. While regulatory and trade proposals can be implemented outside of congressional approval, proposals on taxes and health care will require the approval of Congress. If a single party controls both the presidency and Congress, we could see more significant changes. But there are still limits as to what changes can be effected with a simple majority.
Political bias and economic outlook
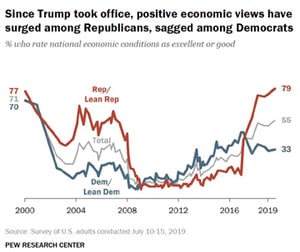
Despite the limitations of divided government, many investors allow their political bias to affect their outlook on the economy. The two charts to the right show people’s views of the current economy and their outlook based on their political affiliation.
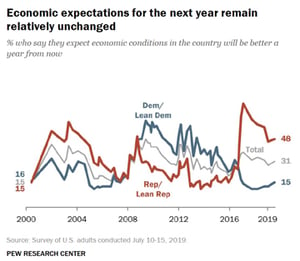 We’ve been in the same bull market since 2009. Yet the 2016 election flipped people’s viewpoints on the economy depending on whether they considered themselves a Republican or Democrat. This bias may have led Republicans to miss out on some of the early recovery, while Democrats may have missed out on the last few years of growth. So, when looking at the outcome of an election, it’s important to understand the implications of possible policies. Don’t overestimate the risks of the other party’s policies when making investment decisions.
We’ve been in the same bull market since 2009. Yet the 2016 election flipped people’s viewpoints on the economy depending on whether they considered themselves a Republican or Democrat. This bias may have led Republicans to miss out on some of the early recovery, while Democrats may have missed out on the last few years of growth. So, when looking at the outcome of an election, it’s important to understand the implications of possible policies. Don’t overestimate the risks of the other party’s policies when making investment decisions.
What does history tell us?
Looking at historical figures in the charts below, you can see that S&P 500 returns were positive in 14 of the past 17 election years, with only two exceptions: the years of the tech bubble bust and the global financial crisis. In the year following an election, however, the picture has been more mixed. Eight of the last 9 years have shown gains, with 6 years of returns in the double digits.
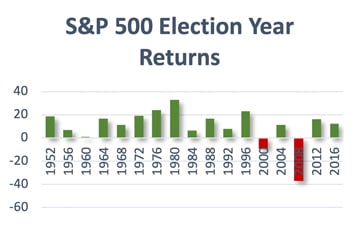
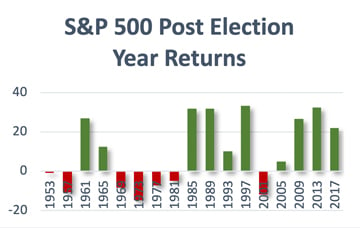 Focusing on fundamentals
Focusing on fundamentals
There is always the possibility that we’ll get a wave election, with big gains by one party that rattle the markets. In the long run, however, the biggest risk to your investments is still a recession, not the outcome of the election. Presidential politics will certainly play a role in the economy, but don’t get caught in election headlines while ignoring investment fundamentals.


 Print
Print

