 Just as I do with the economy, I review the stock market each month for warning signs of trouble in the near future. Although valuations are now high—a noted risk factor in past bear markets—markets can stay expensive (or get much more expensive) for years and years, which doesn’t give us much to go on timing-wise.Of course, there are other market risk factors beyond valuations. For our purposes, two things are important: (1) to recognize when risk levels are high, and (2) to try and determine when those high risk levels become an immediate, rather than theoretical, concern. This regular update aims to do both.
Just as I do with the economy, I review the stock market each month for warning signs of trouble in the near future. Although valuations are now high—a noted risk factor in past bear markets—markets can stay expensive (or get much more expensive) for years and years, which doesn’t give us much to go on timing-wise.Of course, there are other market risk factors beyond valuations. For our purposes, two things are important: (1) to recognize when risk levels are high, and (2) to try and determine when those high risk levels become an immediate, rather than theoretical, concern. This regular update aims to do both.
Risk factor #1: Valuation levels
When it comes to assessing valuations, I find longer-term metrics—particularly the cyclically adjusted Shiller P/E ratio, which looks at average earnings over the past 10 years—to be the most useful in determining overall risk.
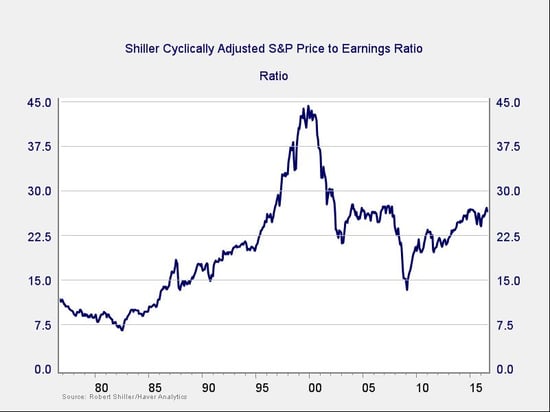
Two things jump out from this chart. First, after the pullback at the start of the year, valuations are again approaching the levels of 2007–2008 and are above the levels of 2015, where previous drawdowns started. Second, even at the bottom of the recent pullback, valuations were still at levels above any point since the crisis and well above levels before the late 1990s.
Although close to their highest point over the past 10 years, valuations remain below the 2000 peak, so you might argue that this metric is not suggesting immediate risk. Of course, that assumes we might head back to 2000 bubble conditions, which isn’t exactly reassuring.
Risk factor #2: Changes in valuation levels
As good as the Shiller P/E ratio is as a risk indicator, it’s a terrible timing indicator. One way to remedy that is to look at changes in valuation levels over time instead of absolute levels.
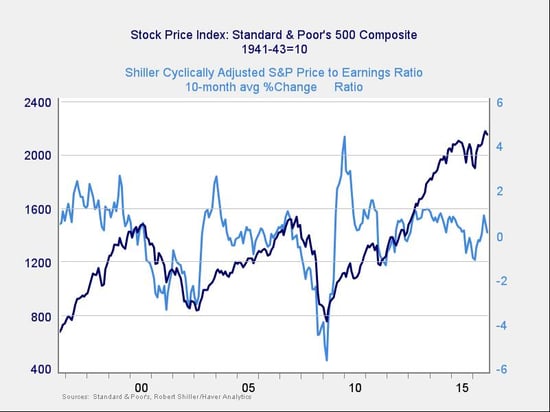
Here, you can see that when valuations roll over, with the change dropping below zero over a 10-month or 200-day period, the market itself typically drops shortly thereafter. With the recent recovery, we moved back out of the trouble zone, and though the trend has turned negative again, we are still in positive territory. Although this metric bears watching, any risks may not be immediate.
Risk factor #3: Margin debt
Another indicator of potential trouble is margin debt.
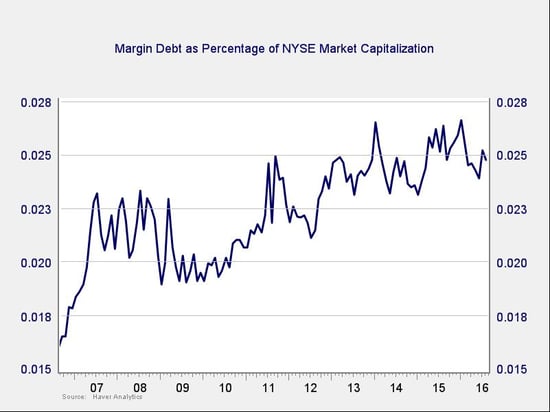
Thanks to the market recovery and some de-risking by borrowers, debt levels (as a percentage of market capitalization) have declined substantially. Though they remain high by historical standards, they are moving down to the lows of the post-crisis years, which suggests risk is receding. I think this continues to be an indicator of somewhat higher risk—but, with recent improvements, not necessarily immediate risk.
Risk factor #4: Changes in margin debt
If we look at the change over time, spikes in debt levels typically precede a drawdown. Even as the absolute risk level remains high, the immediate risk does not, as the spike in debt that led the most recent pullback has come down.
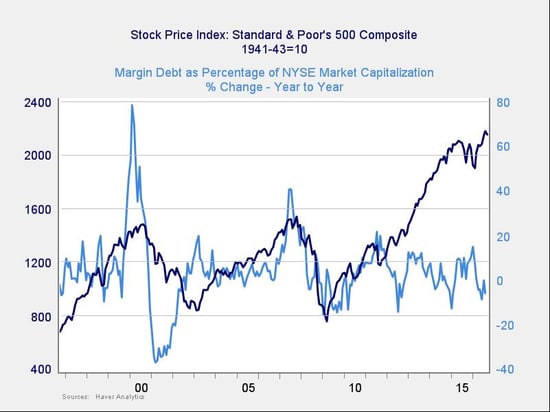
Though the absolute level of margin debt is high, and so is the risk level, the trigger remains far away.
Risk factor #5: The Buffett indicator
Said to be favored by Warren Buffett, the final indicator is the ratio of the value of all the companies in the market to the national economy as a whole.
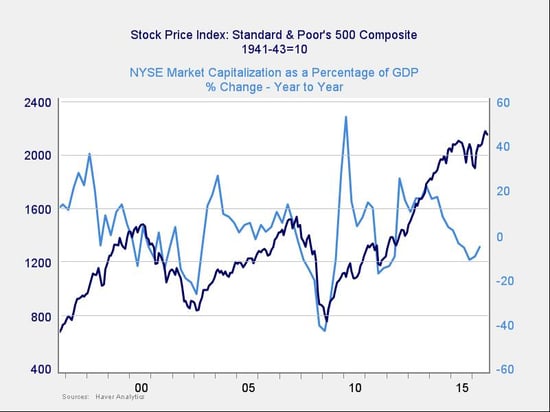
On an absolute basis, the Buffett indicator is actually somewhat encouraging. Although it remains high, it has pulled back to less extreme levels. On a change-over-time basis, however, downturns in this indicator have typically led market pullbacks—and once again, we see that here. With the recent uptick, though, this indicator also suggests the risks are not immediate.
Technical metrics are reasonably encouraging, with all three major U.S. indices well above their 200-day trend lines. Even as markets remain close to new highs, it’s quite possible that the advance will continue. A break into new territory could actually propel the market higher, despite the high valuation risk level.
On balance, all of the metrics are in what has historically been a high-risk zone, so we should be paying attention. But, as I’ve said many a time, there’s a big difference between high risk and immediate risk—and it is one that’s crucial to investing. As it stands, none of the indicators suggests an immediate problem, and several suggest risk may be receding.


 Print
Print


