 Recent equity market volatility is being partially attributed to potential Fed tightening, as the Fed has signaled a shift from an accommodative monetary policy stance to one that is more restrictive. It is doing so in response to the recent hot inflation reads and a rebound in inflation expectations. In general, equities are considered a hedge against inflation. Why, then, are equity investors so concerned? The reason is that not all equity sectors are created alike. Specifically, some can combat inflation and subsequent interest rate increases better than others.
Recent equity market volatility is being partially attributed to potential Fed tightening, as the Fed has signaled a shift from an accommodative monetary policy stance to one that is more restrictive. It is doing so in response to the recent hot inflation reads and a rebound in inflation expectations. In general, equities are considered a hedge against inflation. Why, then, are equity investors so concerned? The reason is that not all equity sectors are created alike. Specifically, some can combat inflation and subsequent interest rate increases better than others.
Are Equities a Hedge Against Inflation?
When inflation is low and rising, as is generally the case during the start of an economic cycle, it is good for equities. It’s the part of the cycle where an economy is emerging from a recession, economic activity is lifting, consumer demand is picking up, profit margins are rising, and loan growth is gathering steam. This backdrop is generally the most ideal for equities.
As the chart below shows, it leads to stock price gains that beat inflation 9 times out of 10. This is where we were in the second half of 2020 and for most of 2021. U.S. equity gains were strong during this period—outpacing inflation by a wide margin.
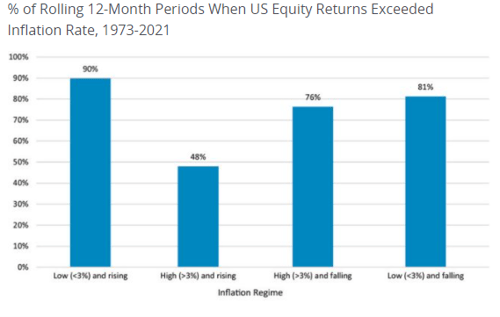
Source: Schroders
If the economy overheats, demand exceeds supply leading to much higher inflation. And if this feeds into higher inflation expectations and interest rates? Things can start to unravel for equity investors. High and rising inflation dents consumer sentiment. Consumers worry that their dollar will not go as far, and they start cutting back on spending. The costs of inputs, labor, and capital rise for companies, but they can no longer pass on these higher costs to consumers. Corporate margins are then compressed, and lower future cash flows get discounted back to the present at higher discount rates, leading to lower stock prices. The market expects that our economy is heading this way, and it’s what is scaring investors.
Not All Sectors Are Created Alike
It is true that high and rising inflation can be a headwind for equities. But some sectors are better at combating inflation than others.
Sectors that do well during higher inflationary regimes are ones that can mitigate rising input costs by passing on the higher prices to consumers. The energy sector stands out in this category. This makes sense, as the profitability of energy companies is tied to the price of oil, and higher oil prices get passed on to consumers. If monetary policy is tightened to manage higher inflation, it could benefit financials as they are positively correlated to interest rates. Consumer staples also tend to hold their own during an inflationary regime as demand for staples generally tends to be inelastic.
Sectors such as technology and consumer discretionary, on the other hand, tend to perform poorly when inflation remains stubbornly elevated. Many technology companies have high growth potential but low current earnings and cash flows. When the cash flows that might be generated in the distant future get discounted back to the present value at a higher discount rate, it leads to lower current intrinsic value of the companies’ stocks. When inflation takes a bite out of the consumer’s pocket, the first expenses to be cut are the discretionary ones, the ones that are dispensable. This dings the revenues and earnings of consumer discretionary companies and pressures their stock prices.
Has Inflation Peaked?
Many of the underlying components of the recent spike in inflation are transitory and may mean revert. Also, plain mathematics suggests that once the jump in activity and prices from the pandemic restart are fully captured, and we enter a more normal economic environment, base effects would cause a moderation in the hot inflation reads. But, as we have started to appreciate in this economic cycle, several sticky components of inflation have also risen (e.g., wages and housing prices).
Historically, inflation that is high but may decelerate to above-average rates has benefited value stocks more than growth stocks. We have already started to see this in the sector rotation. Year-to-date, energy and financials are outperforming, while the interest rate-sensitive sectors like technology, communication services, and real estate are down by a wide margin.
Value Having Its Day in the Sun
Outside brief windows of outperformance, value stocks have been out of favor for a very long time. They are finally having their day in the sun, and this might last a little longer this time as higher inflation and interest rates may persist. This situation, combined with more attractive valuation, may keep momentum strong for these sectors.
Thus, it is important to understand that high inflation and interest rates can be headwinds for equity investors. But some sectors are better positioned for these factors and may outperform while inflation, inflation expectations, and rising interest rates are in play.


 Print
Print

