 With stocks hitting new highs today, even as the pace of economic growth seems to be slowing, much of the market’s strength appears to be coming from the continued low interest rates provided by the Federal Reserve. Although we don’t know when rates will rise, the general consensus seems to be that it will happen sometime this year.
With stocks hitting new highs today, even as the pace of economic growth seems to be slowing, much of the market’s strength appears to be coming from the continued low interest rates provided by the Federal Reserve. Although we don’t know when rates will rise, the general consensus seems to be that it will happen sometime this year.
With that in mind, it’s time to take another look at what happens when rates start to rise, a topic I originally addressed last year.
More specifically, let’s consider this: what might happen to our investments—stocks, bonds, and everything else—when interest rates are finally allowed to return to their natural level? It is an excellent question, one that will affect everyone who holds these securities (which is to say, almost everyone).
In fact, it consists of several sub-questions that should be addressed separately.
- What is the natural level of interest rates?
- What's keeping current rates away from the natural level?
- Will that stop? When?
- What happens when it does stop?
- What does that mean for our investments?
Let‘s start with question 1: what is the natural level of interest rates?
Interest rates defined
Interest rates are actually the price of money. As such, they change with the balance of supply and demand for money. Unlike with most goods, though, there is a monopoly provider of money that can and does change the supply whenever it wants—the Federal Reserve, or, more generally, the central banks. Interest rates are therefore a market, but a manipulated one.
Despite this manipulation, though, there is such a thing as the natural interest rate, one that balances supply and demand. Economic research has defined it, loosely, as the rate of interest on loans that is neutral with respect to prices, and will not tend to either raise or lower them. (A summary is available here.) This is a vague but useful definition, as it situates interest rates squarely within the Federal Reserve’s current policy preoccupation with deflation.
Calculating the natural interest rate
The Fed’s current stimulus policy is directed at lowering rates by injecting money into the economy via buying bonds. According to basic economics, increasing the supply of money should lower the price (interest rates). It should also act to increase prices, which suggests the lowered rates are below the natural rate, consistent with the definition above.
Depending on how you calculate it, the natural rate of interest comes in around 3 percent. Given the uncertainty inherent in this type of work, that means somewhere between 2 percent and 4 percent. Note that this is a real rate, so we have to add inflation back in, which gives us a nominal natural interest rate of around 4 percent to 6 percent at the moment, theoretically.
A look back at history
Using the Berra theorem—the well-known economist Yogi Berra’s idea that theory and practice are the same in theory but different in practice—we can then compare this to real historical interest rates to see if it makes empirical sense. The chart below shows the rates paid by inflation-adjusted Treasury bonds.
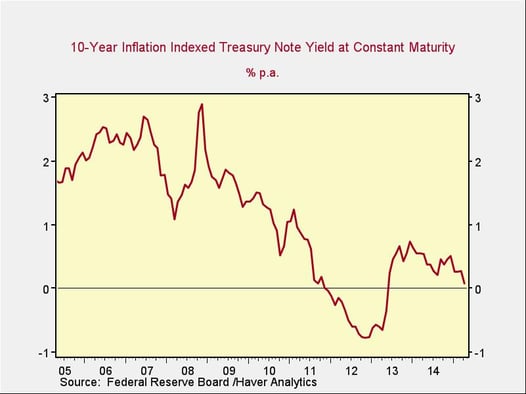
The general range, of around 2 percent to 3 percent before the financial crisis, supports the economic arguments and the decline during the crisis. Add 2 percent to 3 percent for inflation, and we’re right back to the 4 percent to 6 percent that economic theory suggests. The lower rates during and since the crisis largely appear to be due to a “flight to safety” and central bank actions to flood the markets with money, and therefore seem less indicative of normal rate levels.
Comparing the natural nominal rate of, say, 5 percent with the current rate of around 2.22 percent for the 10-year Treasury bond tells us that, yes, current rates are well below what they “should” be. The Fed has apparently succeeded in its aim, to lower rates below the natural level, but it’s not quite that simple, which brings us to question 2. We’ll take a closer look at that tomorrow.


 Print
Print


